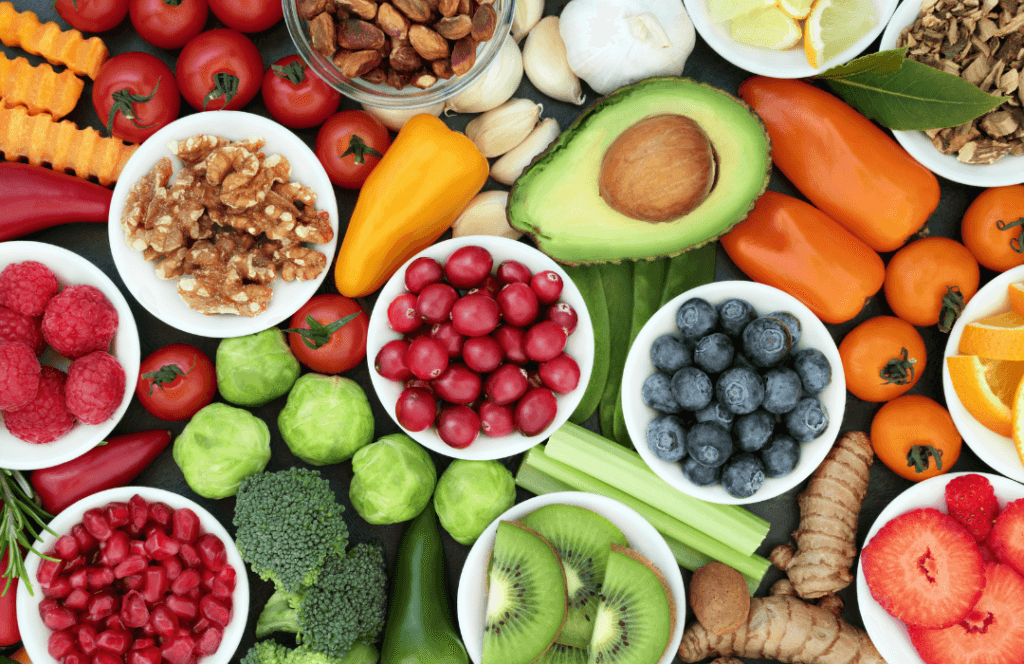
You might be loyal to a skincare routine, but have you thought about how your grocery list affects your glow? When it comes to healthy, radiant skin, what you eat can make a big difference. From fruits and veggies to proteins and healthy fats, each class of food plays a unique role in boosting your skin health. This guide will take you through different food classes and how they help you achieve that healthy, natural glow.
1. Fruits: The Skin’s Sweet Treat
Fruits are often packed with antioxidants, vitamins, and water content, all of which are great for your skin. Many fruits are rich in vitamin C, a powerful antioxidant that promotes collagen production and protects your skin from environmental stressors.
Some top fruits to add to your skincare diet include:
- Berries (Blueberries, Strawberries, Raspberries): These little guys are rich in antioxidants, which help fight the effects of free radicals and slow down skin aging.
- Oranges, Lemons, and Kiwis: Citrus fruits are packed with vitamin C, which is essential for collagen production, giving skin that plump and firm look.
- Papaya and Pineapple: These tropical fruits contain enzymes (like papain and bromelain) that help with gentle skin exfoliation and improving skin tone.
- Watermelon: With its high water content, watermelon is super hydrating, and hydration is one of the best ways to keep your skin smooth and glowing.
Pro Tip: Try adding a fruit bowl or smoothie to your daily diet. Not only is it delicious, but your skin will love the variety of nutrients!
2. Vegetables: The Ultimate Skin Supporters
Vegetables are nutrient-dense and often low in calories, making them ideal for any skin-healthy diet. Many veggies are packed with skin-boosting vitamins and minerals, as well as fiber, which aids in digestion—a clear digestive system often means clearer skin.
Some standout veggies for skin include:
- Carrots, Sweet Potatoes, and Pumpkins: These orange veggies are loaded with beta-carotene, which your body converts to vitamin A. Vitamin A is essential for skin repair and can help prevent clogged pores.
- Spinach and Kale: These leafy greens are rich in vitamin E and iron, both of which contribute to healthy skin cells. They also provide a variety of antioxidants that protect your skin from oxidative damage.
- Bell Peppers: Red and yellow bell peppers are high in vitamin C, which is essential for collagen production and maintaining the elasticity of your skin.
- Tomatoes: Rich in lycopene, tomatoes can provide some natural sun protection for your skin and reduce the effects of UV damage.
Pro Tip: Try roasting or lightly steaming veggies to keep more nutrients intact, or add them to smoothies for an extra dose of greens!
3. Proteins: Building Blocks for Beautiful Skin
Protein is essential for repairing and building tissues, including the skin. Collagen and elastin, which give skin its structure and elasticity, are made up of proteins. A protein-rich diet ensures that your skin has the resources it needs to repair itself and maintain a healthy glow.
Proteins to consider for skin health:
- Lean Meats (Chicken, Turkey): These meats are rich in amino acids, which are necessary for collagen production and skin repair.
- Fish (Salmon, Tuna, Sardines): Fatty fish is packed with omega-3 fatty acids, which help reduce inflammation and keep the skin hydrated.
- Eggs: Eggs contain lutein and choline, both of which help with skin elasticity and hydration. Lutein, in particular, is known to protect the skin from oxidative damage.
- Legumes (Chickpeas, Lentils, Beans): Plant-based proteins also contribute to skin health and are especially helpful if you’re looking for non-meat sources of protein.
Pro Tip: Adding lean proteins to your diet, such as fish or legumes, can help balance your skin’s needs without adding unnecessary fats or sugars.

4. Healthy Fats: The Hydration Heroes
Healthy fats are a must for anyone aiming for dewy, moisturized skin. Omega-3 fatty acids, in particular, are known for their anti-inflammatory benefits and their ability to strengthen the skin’s barrier, keeping moisture in and irritants out.
Healthy fats for glowing skin include:
- Avocados: Rich in monounsaturated fats and vitamin E, avocados keep your skin hydrated, soft, and supple.
- Olive Oil: Extra virgin olive oil is packed with antioxidants and helps fight inflammation while keeping skin smooth and moisturized.
- Nuts and Seeds (Walnuts, Almonds, Chia Seeds): These are packed with omega-3s, vitamin E, and zinc, all of which contribute to healthier skin.
- Coconut Oil: While some prefer using it topically, eating coconut oil can also benefit skin by providing healthy fats that help maintain hydration and elasticity.
Pro Tip: A little fat goes a long way! Try adding a handful of nuts to your daily snacks or drizzle olive oil over your salads to give your skin a hydration boost.
5. Whole Grains: Fuel for a Healthy Glow
Whole grains are a great source of fiber, which helps support a healthy gut and balanced digestion. A healthy digestive system can prevent certain skin issues, such as acne or dullness, by ensuring the body’s waste removal process is working efficiently.
Whole grains to add to your skincare diet:
- Quinoa: High in fiber and protein, quinoa contains a range of amino acids that support collagen production.
- Brown Rice: A whole grain rich in antioxidants, brown rice contains ceramides, which help maintain the skin’s moisture levels.
- Oats: Known for their anti-inflammatory properties, oats are also full of B vitamins, which help with skin regeneration and repair.
- Barley: Contains selenium, an antioxidant that protects skin from damage and maintains its elasticity.
Pro Tip: Swap refined carbs like white bread and pasta with whole grains to give your body a more consistent energy source and keep skin clear and radiant.
6. Water: The Ultimate Hydrator
Although it’s not a “class” of food, water deserves a place on this list for its essential role in skin health. Proper hydration keeps your skin plump, helps flush out toxins, and prevents dryness.
Water-rich foods (like cucumbers, celery, and watermelon) are a great addition to a hydrating diet, but remember that nothing beats drinking enough water each day!
Putting It All Together: Building a Skin-Healthy Plate
Eating for your skin doesn’t mean you have to overhaul your entire diet. Start with small swaps—choose a variety of colorful fruits and veggies, switch to whole grains, and add healthy fats and lean proteins. A balanced diet will not only benefit your skin but also boost your energy and overall health.
Remember, skincare starts from the inside. Each class of food has its unique contribution to how your skin looks and feels. So next time you’re thinking of how to elevate your skincare routine, look no further than what’s on your plate!
________
Disclaimer: Health articles on medical conditions are for information only and do not form a basis for diagnosis. We recommend that if you have any concerns, speak to your doctor or pharmacist for further help and guidance.








